Introduction: How to provide an apartment building Internet service using the Guest Internet STAR-6 kit

Anyone wishing to provide an Internet service to a community requires some technical knowledge to install the infrastructure that will connect the Internet service. Guest Internet makes this easy by providing kits with the parts required and detailed instructions to install and configure the equipment.
The community members who want to connect to the Internet service will use a wireless technology called WiFi. A WiFi network must be installed to deliver the WiFi service to the community members.
If the reader wants to read more and get a deeper understanding of the process to deliver WiFi Internet to community members, we have two free e-books that can be downloaded using these links. The links are also on our website.
How to sell Internet mobile broadband:
https://guest-internet.com/pdfs/How to sell Internet mobile broadband (ENGLISH) - J Barker.pdf
How to start a WISP business:
https://guest-internet.com/pdfs/How to start and build a WISP (ENGLISH) - J Barker 2022.pdf
The Internet WiFi service provided inside an apartment building is called Mobile broadband: people with mobile devices or laptop computers connect to a WiFi Hotspot antenna to get Internet access. The mobile users have to be within a short distance of the Hotspot antenna.
The network infrastructure that will provide the Internet service to community members has three parts.
- The Internet service provider. This is the Internet connection that is shared with community members and can use any of the following technologies; ADSL, cable, fiber, wireless point-to-point, geo-stationary satellite, or low earth orbit (LEO) satellite. The Starlink Internet service uses LEO satellites. Ensure that the sharing of the service with the community is within the terms and conditions of the ISP.
- User controller. This is the Guest Internet controller that will manage the access to the Internet service so that many people can share one Internet connection. Use the Guest Internet product to print vouchers where each voucher has a unique access code with parameters of duration of access, maximum upload and download data speeds, maximum upload and download data limits, and the number of people who can used he code, usually 1. The Guest Internet controller shares the Internet service so that a problem called network congestion is avoided, and also ensures that the ISP data volume limits are not exceeded.
- Point to multi-point (PtMP) wireless access point (WAP). This wireless product broadcasts the Internet access as a WiFi wireless signal. Community members who want to get access to the Internet have to connect to this antenna. This antenna must be visible for any person wishing to connect to it; the connection is called line-of-sight. Any obstruction such as a building or tree will block the signal. Community members with mobile devices can connect to this antenna by selecting the WiFi name. The maximum distance of the connection to a mobile device might be in the range of 10 to 20m inside the building.
- Homes are connected with wireless equipment that gives a much longer communication distance. A wireless receiver (called a client premise equipment – CPE) is installed on the roof of the home and points to the PtMP antenna. The PtMP antenna must be visible from the location of the CPE antenna. The distance from the CPE antenna to the PtMP antenna can exceed 1Hm. The CPE antenna connects to a wireless router inside the home and residents connect to the wireless router using WiFi to get access to the Internet.
The network equipment described above is shown in the next diagram. All community Internet services that connect people using WiFi have this design.

A community member who wishes to access the Internet must request or purchase a voucher that has an access code. The person who manages the Internet service prints the vouchers. The voucher is designed using the Guest Internet controller or cloud service and can include a logo plus text. Vouchers are printed on any letter printer. The process of printing vouchers is shown in the next diagram.

A community Internet service is shown in the next figure. The PtMP antenna is installed on a high point in or close to the community so that all members of the community can see the antenna. The installation might be on a hill, a tall building or a tower. When Starlink is the ISP service then the Starlink antenna is installed close to the PtMP antenna also at a high point so that the Starlink antenna has 180 degree visibility of the sky. The PtMP antenna connects to the Guest Internet controller, which controls access to the Internet. The Guest Internet controller connects to the Starlink router. The antenna on each home points to the PtMP antenna.

The installation with the Starlink antenna is shown in the next diagram.

A location that is ideal for the antenna installation may not have power, and so the installation can be powered using solar panels. A solar panel with battery and charger system with a rating of 500 Watts is required to power the Starlink antenna, the Guest Internet controller and the PtMP antenna.
The community member with a mobile device who wants to connect to the Internet service must first get a voucher with an access code.
The next step is to connect the mobile device WiFi to the PtMP antenna by selecting the name of the WiFi (the SSID) using the mobile device.

The next step is to open a browser to see the login page, an example of a login page is shown in the next figure.

The code on the voucher is typed into the login page then the button is clicked. If the code is valid then the person gets access to the Internet.
Contents of the STAR-6 kit
The STAR-6 kit connects to a Starlink antenna or any other Internet service and provides a controlled WiFi Internet service that can be provided for, or sold to a community. The STAR-6 kit shares the Internet service between many people.
There are two products included with the STAR-6 kit.
- The GIS-R2 Internet controller: this controls the Internet access, generates access codes and prints vouchers with access codes that can be sold to members of the community.
- The WAP-3 wireless access point is a powerful outdoor wireless WiFi transmitter that should be installed at a high point for the maximum range of transmission.
The diagram shows how the products are connected together. The Starlink antenna is not included.

First configure the GIS-R2 Internet controller
The GIS-R2 product includes the quick-start guide in Spanish and English. Please read the quick-start guide before proceeding.
Please download the product manual using this link.
https://www.guest-internet.com/pdfs/GIS_product_manual_(English)_1.1.24.pdf
Or open our website and click on the manual link at the top right of the page.
www.guest-internet.com
Have the manual available and consult when you need more information about the steps in this document. This document describes the features required to start providing an Internet service to community residents. There are many other features such as failure monitor that can be enabled. Consult the manual to find out how to configure these features.
The GIS-R2 must be connected to the Internet to configure the product. Connect your computer to the GIS-R2 LAN1 port using an Ethernet cable as shown in the next diagram.

With your computer LAN port connected to the GIS-R2 LAN1 port open the computer browser, type ‘aplogin.com’
The quick start wizard screen will open, like the screen shown in the figure.
First, select the language top right, English or Spanish.
Click the button to proceed.

Verify that the GIS-R2 has an Internet connection, the figure at the top right must be green, if it is red then stop and get a good Internet connection. The setup procedure can only continue with a good Internet connection.
Next enter a strong password to prevent unauthorized access, make a note of the password.

The next step is to configure the login screen. Select the background and enter the information requested.
This page will display your information in the captive portal. If you want to sell Internet access then explain where the access code vouchers can be purchased. You can add announcements and other information about your service.
Click the button at the bottom of the page when finished.

Next select controlled access. This will require the user to enter a code after opening the login page.
Add any message that should appear on the login page.
Click the button at the bottom of the page.

Click the button to complete the setup process and reboot the unit.

After reboot, open a new browser tab and login as the administrator to complete the setup procedure.
Aplogin.com
Username: admin
Password: set during setup

Enable the GIS-R2 cloud management so that it can be assigned to a cloud account later.
The cloud account will allow you to manage the service remotely and also print access code vouchers using the cloud.

Consult the manual to make any changes to the login page or to create a customized login page.

Installing the WAP-3 wireless access point
The WAP-3 wireless access point is already pre-configured for public WiFi use as follows:
- Wireless name (SSID): Hot Spot
- No WPA encryption configured.
The WAP-3 wireless access point is connected to the GIS-R2 controller as shown in the diagram. The WAP-3 radiates the WiFi signal for mobile users and homes that have a STAR-4 kit installed.
A mobile phone can connect to the WAP-3 wireless access point WiFi signal within a short radius of less then 100m. A home with a STAR-4 kit installed can connect to the WAP-3 when the range is less then 1Km. All wireless connections must be line of sight; a tree or building will block the signal.
The WAP-3 product configuration will be adequate for most applications and so no configuration is required. Skip the configuration and go to the test section.

Configuring the WAP-3 wireless access point
The WAP-3 WiFi product is pre-configured for most community WiFi applications. However the configuration can be changed for different applications. This section describes how to change the configuration. The configuration has three sections.
- Change the wireless name that is transmitted, the SSID. The default is Hot Spot
- Add an encryption key to the wireless transmission.
- Change the password to login to the administrator pages.
If the password is forgotten then press the reset button to return to the factory setting and configure the product again.
To configure the WAP-3, connect a computer as shown in the figure. The computer LAN port must be configured for the static IP address 192.168.188.10.
Open a browser tab and type the login page IP address: 192.168.188.253
The login page will open. Enter the password admin and click login.

After login the home page opens.

Click the wizard tab; verify that the WAP-3 is configured in AP mode

Click the WiFi tab.
On the 2G WiFi menu (2.4 GHz) the wireless broadcast name (SSID) is set as Hot Spot, this can be changed by typing a new name. The WiFi password (WPA encryption key) is set to open so there is no encryption; this is the correct configuration for public WiFi Internet. The WiFi password can be changed to encryption. If this is changed then a password (encryption key) must be added in the box that appears below, the default password is 66666666. After a change click Apply.

On the 5G WiFi menu (5.8 GHz) the wireless broadcast name (SSID) is set as Hot Spot, this can be changed by typing a new name. The WiFi password (WPA encryption key) is set to open so there is no encryption; this is the correct configuration for public WiFi Internet. The WiFi password can be changed to encryption. If this is changed then a password (encryption key) must be added in the box that appears below, the default password is 66666666. After a change click Apply.

Click the advanced menu and select the country region, the default is set to the USA. Select your country from the drop down menu and then click Apply.

The final step is to select the Manage tab and then select the Modify Password menu.

Enter the default password admin and then enter and confirm your new password. When the password has been entered click Save.
Note that if the password has been lost or forgotten then the WAP-3 will have to be reset to the factory default using the reset button and then reconfigured.

Click the right arrow at the top right of the screen to logout of the administration page.
Change your computer LAN port IP setting to DHCP client.
Test the WAP-3 WiFi Internet access when connected to the GIS-R2 and a Starlink antenna
Connect the GIS-R2 WAN port to the Starlink Ethernet connector as shown in the diagram. Connect the WAP-3 WAN port to the PoE power supply and then to the GIS-R2 LAN1 port.
Connect the computer WiFi to the wireless name (SSID) Hot Spot.
Open a new browser tab, type the name of the Guest Internet login page and press enter: aplogin.com.
The login screen should open as shown in the diagram with a box to enter the login code. If there is no Internet access a message will display on the screen. If a login page does not open then go back to the step of testing the computer connection with the GIS-R2.

Two methods of voucher access code printing
Vouchers with access codes can be printed using the Guest Internet controller or using the Guest Internet Cloud to provide codes for a group of controllers.
- Access code vouchers that are printed using the Guest Internet controller can only be authenticated with that controller.
- Any controller in the cloud group can authenticate access code vouchers that are printed using the cloud for a group of controllers.
Before printing any vouchers, the voucher template must be prepared in the controller or the cloud, as described in a previous section.
The procedure to print vouchers is illustrated in the next diagram. Access codes are created using the controller software or the cloud group. The button to print the codes as vouchers is selected. Vouchers are sent to the letter printer attached to the computer. The printed pages are then cut into vouchers and the vouchers can be sold to community residents.

Printing access code vouchers using the Guest Internet controller
Connect your computer to the Guest Internet controller wireless or LAN port and login as the admin using your password.
aplogin.com/admin
Click the ‘manage codes’ menu.

To print vouchers, the code type is set to ‘random’.
Select the number of codes (vouchers) to print.
Select the expiry time, 30 minutes to unlimited.
Select the number of users per code; this is set to 1 by default.
The following parameters are optional.
Select the maximum down and up data speeds that the code will allow.
Set the maximum down and up data byte quantity that the code will allow.
Set the start date and start time of the code if it is not to be used immediately.
Click the button ‘create codes’.

When the codes have been generated then check that the printer is connected and click the button ‘print codes’ to generate the vouchers.
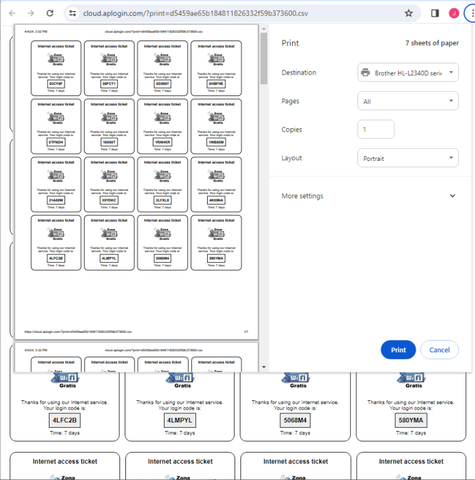
Then click the ‘print’ button to send to the printer.

Print group access code vouchers using your Guest Internet Cloud account

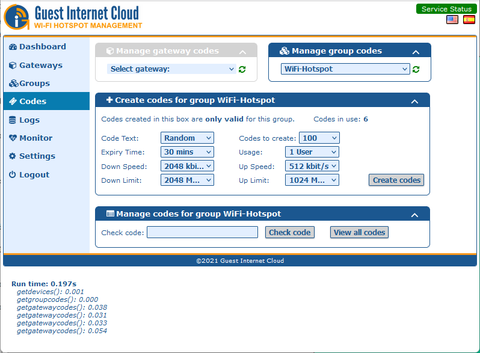
Select the number of codes (vouchers) to print.
Select the expiry time, 30 minutes to unlimited.
Select the number of users per code; this is set to 1 by default.
The following parameters are optional:
Select the maximum down and up data speeds that the code will allow.
Set the maximum down and up data byte quantity that the code will allow.
Click the button ‘create codes’.