All businesses are at risk from a cyber attack. Cybersecurity risks are not well understood by most business owners.
The managers of large businesses are aware of the cybersecurity risks as they have an IT department with engineers who are managing cybersecurity and they plan a budget for the IT requirements to protect the business.

Small and medium businesses use outsourced IT services or use managed service providers. These providers are generally reactive rather than proactive and provide the services that the business owner requests. It is the responsibility of the business owner to be aware of the risks and ensure that the IT service provider delivers the business and technical solutions that will protect the business. The IT services provider must have staff who are skilled and qualified to work with cybersecurity issues. The business owner should be aware that a comprehensive cybersecurity plan has components that are not part of the IT service business deliverables, such as staff cybercrime awareness training. It would be wise for the business owner to seek the services of a cybersecurity provider who can deliver a comprehensive cybersecurity solution.
Lets start by answering some of the questions that business owners should be asking.
- Steal the business data and sell to others.
- Install ransomware to lock the business data, then extort a ransom and receive payment before giving the key to unlock the data.
- Steal the business data then lock the data with ransomware. Demand the ransom to unlock the data then after the ransom is paid demand a second ransom to return the stolen data (double extortion).
- In 35% of cases the criminals do not provide a key to unlock the data after the ransom is paid.
- After the first attack, businesses are at greater risk of a subsequent attack, as the criminal will share the access method with other criminals. A business must upgrade the cybersecurity protection after an attack.
- The average ransomware demand is in the range of $500K to $1M, with the ransom paid in Bitcoin that is difficult to trace.
- When the cybercriminals break into the server they can look at the business accounting system and decide how much the business can afford to pay before demanding the ransom.
- Cybercriminals will put a time limit for the payment of the ransom, after which they will delete the data, or make the data public, or both.
- Businesses with sensitive data that is the property of their clients, pay quickly, these include.
- Healthcare firms (they also have to report a data breach to HHS).
- Accounting firms.
- Legal firms.
- Education systems (although many can’t afford the ransom).
- Larger businesses are also the target of cybercriminals. The preferred targets are listed below.
- Retail businesses.
- Manufacturing businesses.
- Most large business and all banks hire a CISO (chief information security officer) to implement and manage the cybersecurity plan and they invest heavily in cybersecurity to avoid becoming the victim of a cybercriminal.
- If a large business gets attacked by cybercriminals then it is due to bad management decisions regarding IT cybersecurity investments.
What should businesses do immediately after the business data is locked with ransomware?
- Disconnect the network and all devices from the Internet to prevent the criminal doing more damage.
- Call the FBI; if they are familiar with the cybercriminal group then they may have a key to unlock the data.
- Put the recovery plan into action (you did prepare a recovery plan?).
What are the popular cyber attack methods?
- Direct attack from the Internet.
- Attack an access port used by staff to remotely connect to the IT system.
- Phishing to trick users to install a Trojan virus on the computer, which gives the hacker remote access to the computer. Phishing messages are sent via email and SMS for mobile devices.
- Social engineering to steal passwords.
- Attack through a network connected device that bypasses the firewall (called IoT, Internet of Things), for example, a smart A/C system with a 5G remote management port of the type installed in hotels.
- Send flash drives to staff that have a Trojan virus, which installs when the flash drive is inserted into the computer. This works for 40% of the drives sent out to staff. Staff names can be obtained from LinkedIn.
What is the most frequently used method of a cyber attack?
- A phishing attack is popular with cybercriminals. The cyber criminal sends messages impersonating well-known organizations such as banks to the business staff. Each message has a link that when clicked installs a Trojan virus on the computer. The Trojan virus calls the criminal and gives the criminal access to the computer. This method bypasses the network firewall. The user is not aware the cybercriminal is programming the same computer. With access to the computer the criminal can then attack the data servers and encrypt the data files, then demand the ransom. The steps of a phishing attack are shown in the following diagram:
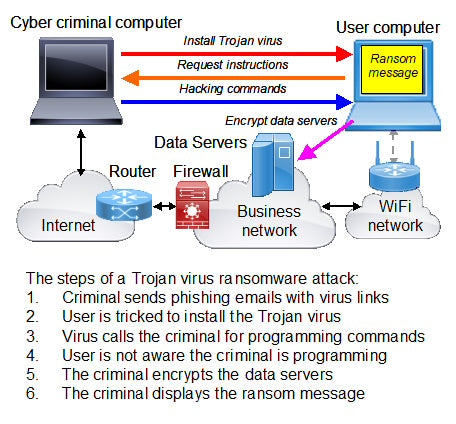
What are the most important parts of a business cybersecurity protection plan?
- Train staff to recognize a potential cyber attack and how to take steps to block the attack.
- Prepare and test a data recovery plan for use if an attack is successful.
- Install cybersecurity measures in the computer infrastructure to block a potential attack.
- Update the cybersecurity plans frequently as cybercriminal methods of attack change; update the training, update the recovery plan, update the computer infrastructure measures. Keep a cyber expert on retainer to give constant advice.
Business IT infrastructure investments that will help to protect the business data from cybercriminals
The technology of computer networks can be confusing with many competing products available. The protection of the business data from cyber criminals adds more confusion, as there are competing cybersecurity technologies and products. Cybersecurity does not have one method of stopping cybercriminals; rather cybersecurity is a collection of methods, products and software that act together to protect different parts of the business network from attack. The most important cybersecurity attack prevention methods are listed below and described in detail. Each item in this list complements the other items and they are deployed collectively to provide strong cybersecurity protection.
- Computer use policy; there are four important considerations.
- Update all software and equipment with security patches when released.
- Install a firewall between the network and Internet to block a direct attack.
- Authenticate only pre-authorized devices onto the network.
- Authenticate users onto the network with 2-factor authentication (2FA).
- Emails are the #1 attack vector; monitor and filter business emails.
- If the network has remote access for staff then secure with VPN and 2FA.
- If the business provides a WiFi Internet service for guests then install a firewall.
- All business recovery plans require daily or hourly offsite data backup.
- Move applications to the cloud where possible for greater security.
- Monitor network access and alert any attempted unauthorized access.
- Does the business network have IoT devices? Verify if any IoT devices have an external link.
The following sections elaborate each of these points in greater detail.
1. Computer use policy, four important points
A business must establish a policy for the computers that are connected to the business network. The purpose of the policy is to minimize the risk of a user computer becoming infected with a Trojan virus. When a Trojan virus is installed on a user computer it will give the cybercriminal access to the computer and any other system on the network, without the computer user knowing that the cybercriminal is sharing the computer.
The four points of computer use policy described below are very important to minimize the possibility of a cyber attack.
- Do not connect any business computer to a different unprotected network. If staff work at the office and at home then provide 2 computers, one for the office and one for home, and share data files via a storage system that checks for viruses.
- Anti-virus software must be installed on all business computers and updated regularly. The anti-virus software may block the installation of the Trojan virus on the computer if the user accidentally clicks a phishing message link.
- Business computer USB ports must be locked with a device, as USB flash memories are an easy way to infect computers. USB locks are available from many sources. One technique used by cybercriminals is to post what looks like a new flash stick to several employees with an Amazon address label where each flash stick has a Trojan virus. The virus is installed on the computer if the flash stick is inserted in the drive. This method works with about 40% of the flash sticks sent out.
- Block access to personal emails on business computers, which is a preferred attack vector to send phishing emails. Personal emails can be found on sites such as LinkedIn. Configure the firewall or an end-point security appliance to block access to email servers.
2. Update all software and equipment with security patches when released
Cybercriminals and security professionals are constantly finding weak points with software and hardware products that can be used as a method to attack the business network data. Cybercriminals call these weak points “exploits” because they can be exploited to gain access. All software manufacturers, like Microsoft, publish frequent updates with security patches that are designed to block access to the weak point that was discovered. Network equipment such as routers have firmware that also requires updates with security patches. Every business needs vigilant IT staff or IT service provider who can identify and install updates for each software and hardware product in the business network. If the patches are not installed then a cybercriminal will use one of the software or hardware weak points to gain access to the business data. Many software products like Windows can be configured to update automatically. Products like routers do not have automatic firmware updates. All businesses should contract a security expert who frequently updates software and firmware with security patches.
3. Install a firewall between the network and Internet to block a direct cyber attack
Many cybercriminals will try a direct attack to the business network using the public IP address. Most network routers are easily hacked because the firmware has not been updated and the exploits or firmware weaknesses are well known within the cybercriminal community. If the cybercriminal is able to pass the router then the next step is to attack the network server and install ransomware.
The installation of a firewall between the ISP router and the business network will block any attempt to access the network when the firewall is properly configured. It is necessary to have the firewall configured by an expert so that it is effective in blocking cybercriminals. Many different types of firewall are available, and they vary in features and performance. The business owner will need to guidance of a cybersecurity professional to select the correct firewall for the business.
It may be necessary to allow access from the Internet for some reason, such as staff connecting to the network remotely. In this case the firewall can open a specific encrypted port to allow remote access. All remote connections should be made using a VPN with strong encryption.
The next figure shows the installation of the firewall in the network.

4. Authenticate all user devices onto the network
The network data is at risk if users are able to connect any computer or mobile device to the network. Such devices might have been connected to the Internet at other locations and compromised with a Trojan virus. The business owner should ensure that only approved devices are connected to the network, and this should be a device that is never connected to other networks. Authentication can be done with the device MAC address, or for extra security verify other parameters, for example the MAC address plus OS type plus browser type. Some products require an encryption key to be installed in the device that will authenticate the device onto the network. Applying strict device access controls adds security to the network.
The next diagram illustrates device authentication using an end-point firewall product.

5. Authenticate all users onto the network
Small and medium business networks allow any user to connect and then have passwords for specific applications. Unfortunately this will not stop a cybercriminal who has planted a Trojan virus onto the user computer. Once the computer is connected to the network the criminal has free access to the server.
Large business networks such as those installed by banks and large e-commerce firms have end point-security, which authenticates users onto the network. Large businesses also install multi-factor-authentication (MFA), which requires a password plus a code. Password only network access is not effective as a security measure because a password can be stolen and used by the criminal to get access to the network data.
MFA combines something that the user knows (a password) with something that the user has (a mobile phone). The user enters the password then receives a one-time-password (OTP) text message on the mobile phone, which is usually a six-digit numerical code. The user then enters the OTP after the password to gain access to the network.
MFA is the single most effective measure to prevent cybercriminals getting access to the business network.
Device and user authentication to access the network is called zero-trust verification. No device or user is trusted until that device or user is authenticated, and the devices and users have to be authenticated each time that they connect to the network.
The access control rules that can be configured with the end-point security might include the following.
Authentication rules
- Verify MAC of device, if approved user can connect.
- MAC not verified, user required to enter password.
- MAC not verified, user required to 2FA with OTP.
- Verify MAC of device, user required to enter password.
- Verify MAC of device, user required to 2FA with OTP.
Filtering rules
- Specify allowed / blocked network IP range.
- Specify allowed / blocked Internet public IP’s /domains.
- Specify category filtering using a system such as a Cisco openDNS subscription.
Monitoring
- Check identified devices in the LAN network, report status.
Reporting
- List the authenticated users.
- List IP requests but not authenticated, check for intruder.
- Failed authentication, send alert to admin.
The next figure shows how the end-point security firewall is installed in the network. End-point security does not replace the Internet access firewall, it complements it to increase the security of the network.

Multi-factor-authentication can have several authentication steps. The popular implementation is 2-factor authentication, which combines a password with an OTP code. 2FA is a good deterrent; when most cyber-criminals see the network has 2FA they give up and move on to the next victim.
The steps for 2-factor authentication are shown in the next diagram.

Microsoft’s VP of identity security, Alex Weinert said the following;
“99.9% of user accounts that are compromised don’t have MFA authorized. Multi-factor authentication is one of the most basic defenses against identity attacks today.”
6. Emails are the #1 attack vector.
Most successful cybercriminal attacks are made using phishing emails. These emails impersonate a legitimate business, such as a bank or a large company like Amazon, and include a link or an attachment that the person is urged to click immediately to solve some problem. Unfortunately when the link is clicked a Trojan virus is installed on the computer, which then gives the cyber criminal access to the network and business data.
Staff email addresses are easy to find. Many are published on company websites and the cybercriminal can also get email addresses from social media sites such as LinkedIn.
The business has to implement three steps to prevent a phishing attack.
- Staff training to recognize a phishing attack and have an IT person that the suspected attack can be reported to. Repeat the training frequently. The business should hire a cyber security professional to provide the training.
- Install a business email server that can remove links and attachments from business emails. It is necessary to provide staff with a secure method to transfer files between staff members and between staff and people outside the company. All banks have such a system implemented as they are the targets of criminals. Small and medium business should also scan business emails.
- Block access to personal email accounts on business computers. Personal emails are the preferred method for attack by cyber criminals and the personal emails can be obtained via social media. Staff can access personal emails using their mobile devices that have no connection to the business network.
Access to personal emails can be blocked with the business Internet firewall or with the end-point security product.
The following diagram illustrates the network configuration with email server and website blocking.

7. Does the network have remote access for staff?
Many businesses have staff that travel or work from home part time. The business therefore provides a remote access facility for staff to connect to business systems so that they can work remotely. The remote access port is one of the targets for cybercriminals who can use the port to get access to the network servers and to the business data.
The remote access port is opened in the Internet firewall however the port requires two security measures to ensure that cybercriminals do not get access.
- The connection is made via a VPN tunnel using strong security encryption with the staff computer having a unique key for the VPN client.
- The remote user requires a MFA login process to verify the authenticity of the user. This means that the user will login with a password, then receive an OTP on a mobile phone, and then enter the OTP to gain access to the network.
With the zero-trust procedure, the remote user has to be authenticated each time that the user connects to the network.
The next diagram illustrates the remote access network configuration.
8. Does the business provide a public Internet service for guests?
Many businesses provide a WiFi Internet service for guests and visitors.
- Motels, hotels, resorts.
- Coffee bars, restaurants.
- Retail businesses.
- Campgrounds, RV parks.
The guest connects to one or more wireless access points that are connected to an ISP service, the business computers may be connected to the same ISP. A cybercriminal can connect to the guest WiFi and then get access the business network computers. The cybercriminal does not have to be physically present to access the business network. There is a probability that guest computers or mobile devices have a Trojan virus installed and so the cyber criminal is waiting for the user computer to connect to a network.
A firewall must be installed between the guest WiFi and the business network in order to block any attempt to access the business network.
If the business network has a point of sale (PoS) terminal then the card companies require that the PoS is isolated from any public access network. The merchant has to comply with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) and either connect the public WiFi to an ISP different from the business ISP, or else isolate the public network with a firewall.
Some Hotspot controllers that businesses can install to manage the guest WiFi also have a firewall that is compliant with PCI DSS.
9. All businesses need a cyber attack recovery plan
Many data protection methods can be included in a network to minimize the probability of an attack, however it is impossible to prevent an attack from determined cybercriminals. The reason is that cyber criminals continuously develop and share new techniques of attack, and look for weaknesses in software such as Windows. When hackers find a weakness it might be a week before Microsoft issues an upgrade patch. Businesses that don’t install security patches are at risk from a successful attack. Cybercriminals work quickly to take advantage of any opportunity.
All businesses must have a recovery plan in case that a cyber attack is successful and the business data is locked with ransomware. The purpose of the recovery plan is to restore the business data after a ransomware attack and avoid paying the ransom. The recovery plan has the following steps.
- The backup plan must be prepared with an IT service supplier that is on a retainer, to store and recover the data when requested.
- Transfer the business data frequently to an offsite storage server using an encrypted connection. The frequency may be each day or each hour. Each backup must be stored for a minimum period of 1 to 3 months. If the business database is encrypted with ransomware then the last few backups are also likely to be encrypted. The backup server must not be accessible within the business network, as the cybercriminal will try to lock the backup data first.
- Server disk drives are prepared with all business software, these can be a mirror of drives installed in the servers. Have at least 2 sets of drives.
- In the event of a ransomware attack the IT service provider is called to restore the network, and the procedure is as follows.
- Disconnect the network from the Internet to prevent further criminal access.
- Advise the FBI as they may have information about the ransomware attack.
- Swap all server drives with the backup drives.
- Restore a clean copy of the data from the offsite storage
- Before the network can be reconnected to the Internet the method of access used by the criminals must be found, this might be the workstation where the ransom message is displayed.
- If end-point security is installed in the network then that will have a log of workstation access to the network, and might help to identify the workstation that was used by the cybercriminals.
- It may be necessary to replace disk drives in all workstations if the workstation with the Trojan virus is not found.
- After the network is restored and the Internet reconnected, carefully monitor what is happening with data over the network, as the criminal will try to attack again.
The recovery process may take from a few hours to a few days depending on the configuration of the business IT systems. During this time the business may not be able to function. The business owner should request the IT service provider who is implementing the recovery to explain the occurrence to staff at the first opportunity and explain the recovery process.
It will be necessary for the IT service provider to review and update security procedures to prevent a similar occurrence.
The next diagram illustrates the offsite backup storage data connection.

10. Move applications and data to the cloud where possible
Move application programs from servers within the business to a cloud storage vendor where possible. There are several popular cloud vendors that include Microsoft Azure and Amazon AWS. There are several advantages of having the applications software in the cloud, the important reasons are listed below.
- Cloud cybersecurity is very strong, cloud vendors have cybersecurity experts who are constantly monitoring network use and have advanced tools such as AI to alert potential attack situations.
- Remote workers connect to the cloud, and no longer require remote access to the business network, which reduces the risk of attack to the business network. However the business network requires security measures as a Trojan virus installed on a staff computer will give the cybercriminal access to the cloud software and the criminal will then look for weaknesses (exploits) with the software.
Some popular software applications like QuickBooks have a cloud version and the transition from the desktop version to the cloud version may take less than 1 hour. Custom software applications developed for or by the business will require effort to migrate to a cloud service. The business owner should contract with a specialist service provider who has expertise with the chosen cloud service vendor and can provide references for successful software migration services.
The next diagram shows the network with cloud-based business applications.

11. Monitor network access
End-point security firewall tools provide a means of monitoring all accesses to the business network, including both successful and failed access attempts. User access should require 2-factor authentication. It is important to monitor failed access attempts as this might be a cybercriminal attempting to access the network. It should be possible to alert the network administrator when a failed attempt to access the network occurs. The end-point security firewall should log all access to the network with a time and duration stamp, and provide a report on request. When the end-point security firewall has cloud management then the IT service provider can monitor and manage the business network remotely.
The next figure illustrates the use of an end-point security firewall to monitor access to the network.

12. Does the business network have IoT devices?
One method of attacking the business network that cyber criminals may attempt is access to an IoT (Internet of Things) device that is connected to the network and has Internet access. IoT (Internet of things) is a broad category that includes all types of computer equipment that operates unattended. Often businesses are not aware that IoT equipment is communicating over the Internet and may provide a point of access for cybercriminals. A few types of Internet and network connected IoT devices are listed below.
- Network printer with a manufacturer maintenance service.
- Network connected A/C controller with supplier remote access.
- Manufacturing equipment connected to the network and with remote support from the supplier.
IoT devices share some common characteristics.
- IoT devices have limited or no cybersecurity security controls.
- IoT device firmware is rarely updated with security patches.
Business owners should note that many business attacks are made via an attack to a supplier or customer of the business, and through the network connection are able to attack the owners business. Therefore an attack may be made following an attack to a supplier business that maintains the A/C service for example. Business owners may be surprised that an attack can be made via an A/C system, however many hotels and businesses have network connected A/C that permits an app to control the A/C and will switch off the A/C of a room that is not occupied.
The business owner should request the IT service provider to document IoT devices that are connected to the business network. This can be tracked through IP addresses of network-connected devices.
IoT devices should connect to the network through the end-point security firewall so that the IoT accesses are logged and the units can be monitored.
The connection of IoT devices to the business network is illustrated in the next figure.

Summary
There are several points that summarize this document:
- The twelve points listed here should be implemented together where appropriate.
- Cybersecurity investments are a consequence of using computers and the Internet to do business. The business will also put locks on the premises doors and install a CCTV system with intruder alarm.
- Although implementing cyber security precautions has a cost for the business, the cost will be much less than any ransom demand.
- If a business seeks cyber security insurance against a cyber attack the insurer will require that the points listed here are implemented in order to qualify the business for insurance.
- It is very important that cybersecurity measures are updated and replaced, as the technology develops to insure the best level of protection.
Any questions can be addressed to Internet Technology Answers Inc. at the following email address: info@Internettechnologyinc.com
The products described in this article can be found at the following Guest Internet distributors:
Wispzone: https://www.wispzone.com/
Flytec: https://flyteccomputers.com/
Kommago: https://www.kommago.nl/
Syscom: https://www.syscom.mx/
Epcom: https://www.epcom.net/
Solwise: https://www.solwise.co.uk/


